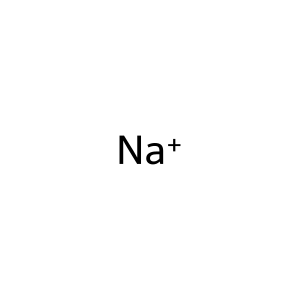Reaction: SLC6A5,9 cotransport Gly, Cl-, Na+ from extracellular region to cytosol
- in pathway: Na+/Cl- dependent neurotransmitter transporters
The amino acid glycine plays an important role in neurotransmission. Its action is terminated by rapid re-uptake into the pre-synaptic terminal or surrounding glial cells. This re-uptake is mediated by the sodium- and chloride-dependent glycine transporters 1 and 2 (GLYT1 and GLYT2 respectively). GLYT1 is encoded by the human gene SLC6A9 and is expressed in the brain, liver, kidney, pancreas, lung and placenta (Kim KM et al, 1994). GLYT2 is encoded by the human gene SLC6A5 and is predominantly expressed in the medulla (Morrow JA et al, 1998). Defects in SLC6A5 cause startle disease (STHE or hyperekplexia). STHE is is a human neurological disorder characterized by an excessive startle response (Rees MI et al, 2006).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
Na+ [cytosol]
Cl- [cytosol]
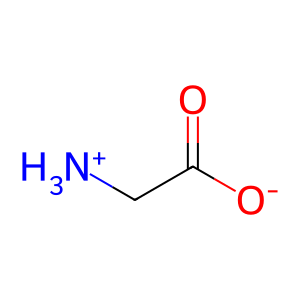
Gly [cytosol]
Cl- [extracellular region]
Gly [extracellular region]
Na+ [extracellular region]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-444120
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
chloride
glycine zwitterion
sodium(1+)
Reaction output - small molecules:
sodium(1+)
chloride
glycine zwitterion
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-444120