Reaction: Addition of N-acetyl-D-glucosamine to Dolichyl phosphate
- in pathway: Biosynthesis of the N-glycan precursor (dolichol lipid-linked oligosaccharide, LLO) and transfer to a nascent protein
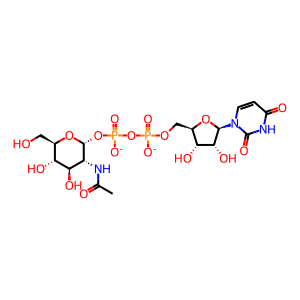
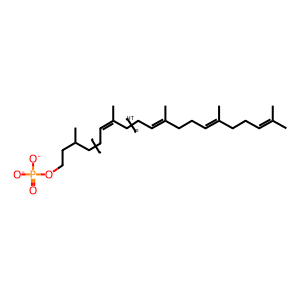
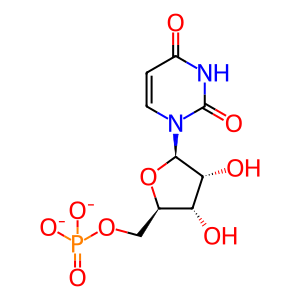
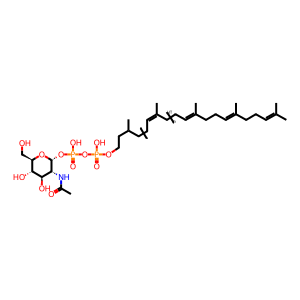
In the first step of N glycan precursor (LLO) synthesis, N acetylglucosamine is added, via an alpha 1,3 linkage, to a molecule of dolichyl phosphate, producing N acetyl D glucosaminyl diphosphodolichol (Eckert et al. 1998). This reaction is catalyzed by DPAGT1 (ALG7 in yeast), mutations in which are associated with CDG disorder type I J (Wu et al. 2003) and with congenital myasthenic syndrome with tubular aggregates type 2 (Belaya et al. 2012). The dolichyl phosphate acts as an anchor for the LLO, so that subsequent sugar addition reactions take place on a sugar anchored in the ER membrane.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
UMP [cytosol]
GlcNAcDOLDP [integral component of cytoplasmic side of endoplasmic reticulum membrane]
UDP-GlcNAc [cytosol]
DOLP [integral component of cytoplasmic side of endoplasmic reticulum membrane]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-446191
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosamine(2-)
dolichyl phosphate(2-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
uridine 5'-monophosphate(2-)
N-acetyl-D-glucosaminyldiphosphodolichol
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-446191