Reaction: Transfer of N-glycan to the protein
- in pathway: Asparagine N-linked glycosylation
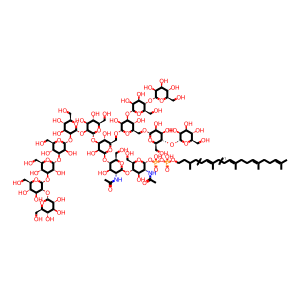
The 14-sugar N-glycan precursor (aka lipid-linked oligosaccharide, LLO), synthesized in the previous reactions, is attached in a single step to a nascent protein, releasing the dolichyl phosphate anchor and the as-yet unfolded glycoprotein. The reaction occurs cotranslationally as the growing peptide chain leaves a ribosome associated with the ER membrane and enters the ER lumen. This reaction is catalyzed by the oligosaccharyltransferase (OST) complex, comprising at least seven proteins; DAD1 (Dolichyl-diphosphooligosaccharide--protein glycosyltransferase subunit DAD1), DDOST (OST48 in yeast), RPN1 (ribophorin 1), RPN2 (ribophorin 2), OST4, TUSC3 (N33), MAGT1 (magnesium transporter protein 1) and either STT3A or STT3B (Dolichyl-diphosphooligosaccharide--protein glycosyltransferase subunit STT3A and B), which contain the catalytic domain (Kelleher & Gilmore 2006). A mutation in RPN2 is associated with CDG-Ix (Vleugels et al. 2009). The signal for glycosylation is the consensus sequence Asn - X - Thr/Ser, where the first amino acid is always Asn, the second can be any amino acid except for Pro, and the third position may be Thr, Ser or Cys, with a preference for the first (Breuer et al. 2001). Not all Asn - X - Thr/Ser sites are modified in vivo (Petrescu et al. 2004).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
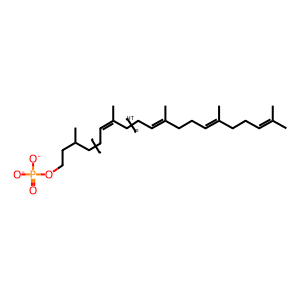
DOLP [integral component of lumenal side of endoplasmic reticulum membrane]
(Glc)3 (GlcNAc)2 (Man)9 (PP-Dol)1 [integral component of lumenal side of endoplasmic reticulum membrane]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-446209
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
glycan G00008
Reaction output - small molecules:
dolichyl phosphate(2-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-446209