Reaction: poly((1,4)-alpha-glucosyl) glycogenin-2 + n orthophosphate => glycogenin-2 + n D-glucose 1-phosphate [PYGL]
- in pathway: Glycogen breakdown (glycogenolysis)
The phosphorylated PYGL dimer (a form) of glycogen phosphorylase catalyzes the reaction of orthophosphate and poly((1,4)-alpha-glucosyl) glycogenin-2 to form D-glucose 1-phosphate and glycogenin-2. This reaction occurs on the surfaces of cytosolic glycogen granules. Non-phosphorylated PYGL dimers (b form) are catalytically inactive even in the presence of AMP. In the body, this reaction takes place in the liver where its dependence on hormonally stimulated PYGL phosphorylation (and lack of sensitivity to AMP) allow glucose mobilization in response to a demand for glucose from the rest of the body (Newgard et al. 1989; Rath et al. 2000).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
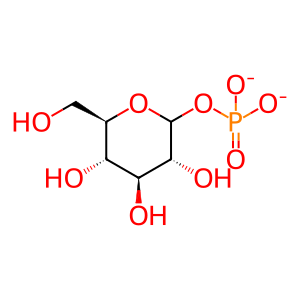
G1P [cytosol]
Pi [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-453339
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
hydrogenphosphate
Reaction output - small molecules:
D-glucopyranose 1-phosphate(2-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-453339