Reaction: Defective DPAGT1 does not transfer GlcNAc to DOLP
- in pathway: Defective DPAGT1 causes CDG-1j, CMSTA2
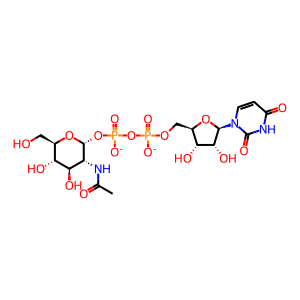
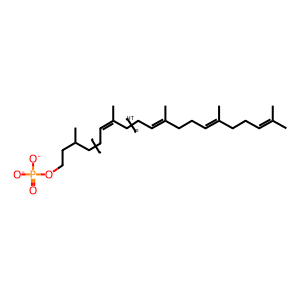
In the first committed step of N-glycan precursor (LLO) synthesis, UDP-N-acetylglucosamine--dolichyl-phosphate N-acetylglucosaminephosphotransferase (DPAGT1) normally catalyses the transfer of N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc), via an alpha-1,3 linkage, to a molecule of dolichyl phosphate (DOLP). Defects in DPAGT1 can cause congenital disorder of glycosylation, type 1j (DPAGT1-CDG, previously called CDG1j; MIM:608093), a multisystem disorder characterised by under-glycosylated serum glycoproteins. Clinical features include defective nervous system development, psychomotor retardation, coagulation diorders and immunodeficiency. Mutations causing DPAGT1-CDG include Y170C, I69N and a G-A transition in intron 1 (not shown here) which results in degradation of the mutant mRNA (Wu et al. 2003, Timal et al. 2012). Defects in DPAGT1 can also cause myasthenic syndrome, congenital, with tubular aggregates, 2 (CMSTA2; MIM:614750 a syndrome that arises from impaired neuromuscular transmission and characterised by muscle weakness, especially of the limb-girdle. Mutations causing CMSTA2 include V117I, M108I, L120M, T234Hfs*116 and V264G (Belaya et al. 2012).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
UDP-GlcNAc [cytosol]
DOLP [integral component of cytoplasmic side of endoplasmic reticulum membrane]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-4549334
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosamine(2-)
dolichyl phosphate(2-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-4549334