Reaction: Defective DPM1 does not transfer mannose to DOLP to form DOLPman
- in pathway: Defective DPM1 causes DPM1-CDG
Dolichyl-phosphate mannosyltransferase (DPM), a heterotrimeric protein embedded in the endoplasmic reticulum membrane, mediates the transfer of mannose (from cytosolic GDP-mannose) to dolichyl phosphate (DOLP), to form dolichyl-phosphate-mannose (DOLPman). The first subunit of the heterotrimer (DPM1) appears to be the actual catalyst, and the other two subunits (DPM2 and 3) appear to stabilise it (Maeda et al. 2000). Defects in DPM1 can cause congenital disorder of glycosylation 1e (DPM1-CDG, CDG-1e; MIM:608799), a multisystem disorder caused by a defect in glycoprotein biosynthesis and characterised by under-glycosylated serum glycoproteins (Kim et al. 2000, Imbach et al. 2000, Garcia-Silva et al. 2004). Frameshift mutations that can cause DPM1-CDG are G111Lfs*45, Q210Rfs*4 as well as the point mutation R92G (Kim et al. 2000, Imbach et al. 2000).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
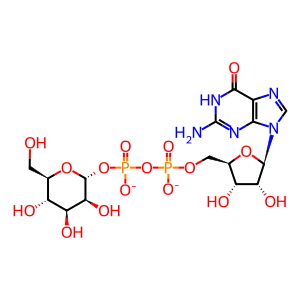
GDP-Man [cytosol]
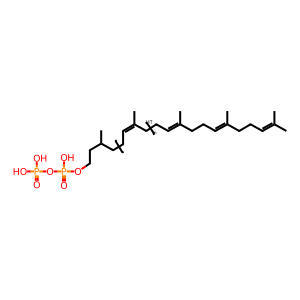
DOLDP [integral component of cytoplasmic side of endoplasmic reticulum membrane]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-4717406
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
GDP-alpha-D-mannose(2-)
dolichyl diphosphate
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-4717406