Reaction: Defective ALG3 does not add mannose to the N-glycan precursor
- in pathway: Defective ALG3 causes CDG-1d
Dol-P-Man:Man(5)GlcNAc(2)-PP-Dol alpha-1,3-mannosyltransferase (ALG3) adds the sixth mannose (although the first to be derived from dolichyl-phosphate-mannose, DOLPman) to the lipid-linked oligosaccharide intermediate GlcNAc(2) Man(5) (PPDol)1 (Korner et al. 1999). Defects in ALG3 are associated with congenital disorder of glycosylation 1d (ALG3-CDG, CDG1d; MIM:601110), a multisystem disorder caused by a defect in glycoprotein biosynthesis and characterised by under-glycosylated serum glycoproteins. CDG type 1 diseases result in a wide variety of clinical features, such as defects in the nervous system development, psychomotor retardation, dysmorphic features, hypotonia, coagulation disorders, and immunodeficiency. (Sun et al. 2005). Point mutations that cause ALG3-CDG are G118D, R171Q, W71R and M157K (Korner et al. 1999, Sun et al. 2005, Kranz et al. 2007).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
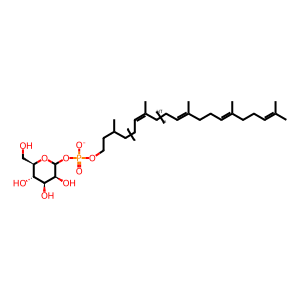
DOLP-Man [integral component of lumenal side of endoplasmic reticulum membrane]
(GlcNAc)2 (Man)5 (PP-Dol)1 [integral component of lumenal side of endoplasmic reticulum membrane]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-4720473
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
dolichyl D-mannosyl phosphate(1-)
glycan G00006
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-4720473