Reaction: Defective ALG12 does not add mannose to the N-glycan precursor
- in pathway: Defective ALG12 causes CDG-1g
Dol-P-Man:Man(7)GlcNAc(2)-PP-Dol alpha-1,6-mannosyltransferase (ALG12) (Chantret et al. 2002) normally tranfers the 8th mannose moiety to the lipid-linked oligosaccharide (LLO aka N-glycan precursor) which is required for subsequent N-glycosylation of proteins. Defects in ALG12 are associated with congenital disorder of glycosylation 1g (ALG12-CDG, CDG1g; MIM:607143), a multisystem disorder caused by a defect in glycoprotein biosynthesis and characterised by under-glycosylated serum glycoproteins (Chantret et al. 2002, Grubenmann et al. 2002). CDG type 1 diseases result in a wide variety of clinical features, such as defects in the nervous system development, psychomotor retardation, dysmorphic features, hypotonia, coagulation disorders, and immunodeficiency. Point mutations that can cause ALG12-CDG are F142V, T67M, R146Q, G101R, L158P and Y414* (Chantret et al. 2002, Grubenmann et al. 2002).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
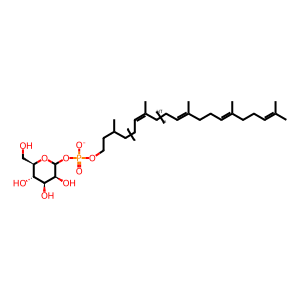
DOLP-Man [integral component of lumenal side of endoplasmic reticulum membrane]
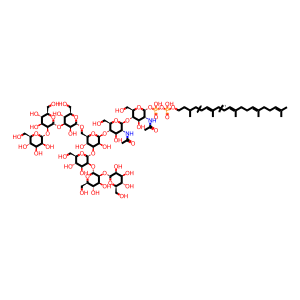
(GlcNAc)2 (Man)7 (PP-Dol)1 [integral component of lumenal side of endoplasmic reticulum membrane]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-4720497
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
dolichyl D-mannosyl phosphate(1-)
alpha-Man-(1->2)-alpha-Man-(1->2)-alpha-Man-(1->3)-[alpha-Man-(1->2)-alpha-Man-(1->3)-alpha-Man-(1->6)]-beta-Man-(1->4)-beta-GlcNAc-(1->4)-alpha-GlcNAc(PP-Dol)
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-4720497