Reaction: Defective DHDDS does not elongate E,E-FPP
- in pathway: Defective DHDDS causes RP59
The ER membrane-associated enzyme dehydrodolichyl diphosphate synthase (DHDDS) (Endo et al. 2003) normally mediates the sequential head-to-tail cis addition of multiple isopentyl pyrophosphate (IPP) molecules to farnesyl pyrophosphate (E,E-FPP) to produce polyprenol pyrophosphate (pPPP) (Shridas et al. 2003). Dolichol in humans contain homologues ranging from 17-23 isoprene units, the most common homologues contain 19 or 20 isoprene units (Freeman et al. 1980). Dolichol is an important substrate in the N-glycosylation of proteins, including rhodopsin.
Defects in DHDDS cause retinitis pigmentosa 59 (RP59; MIM:613861), a pigment retinopathy, characterised by retinal pigment deposits (visible on fundus examination) and primary loss of rod photoreceptors followed by secondary loss of cone photoreceptors. Sufferers typically have night vision blindness and loss of mid to peripheral vision. As the condition progresses, they lose far peripheral vision and eventually central vision (Zuchner et al. 2011). The founder missense mutation K42E in Ashkenazi Jewish ethnicity can cause RP59. The Lys42 residue is highly conserved across different species and is positioned close to the catalytic centre of DHDDS and to its substrate binding site for E,E-FPP (Zuchner et al. 2011, Zelinger et al. 2011).
Defects in DHDDS cause retinitis pigmentosa 59 (RP59; MIM:613861), a pigment retinopathy, characterised by retinal pigment deposits (visible on fundus examination) and primary loss of rod photoreceptors followed by secondary loss of cone photoreceptors. Sufferers typically have night vision blindness and loss of mid to peripheral vision. As the condition progresses, they lose far peripheral vision and eventually central vision (Zuchner et al. 2011). The founder missense mutation K42E in Ashkenazi Jewish ethnicity can cause RP59. The Lys42 residue is highly conserved across different species and is positioned close to the catalytic centre of DHDDS and to its substrate binding site for E,E-FPP (Zuchner et al. 2011, Zelinger et al. 2011).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
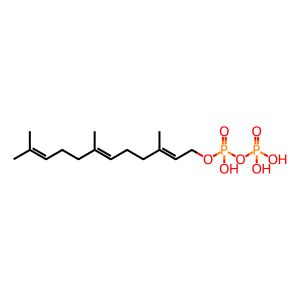
IPPP [cytosol]
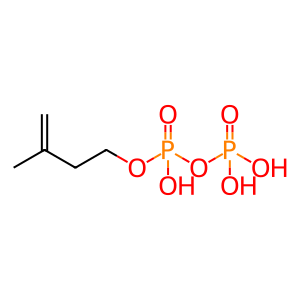
E,E-FPP [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-4755545
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
isopentenyl diphosphate
2-trans,6-trans-farnesyl diphosphate
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-4755545