Reaction: Defective DOLK does not phosphorylate DCHOL
- in pathway: Defective DOLK causes DOLK-CDG
Dolichol kinase (DOLK, TMEM15) normally mediates the phosphorylation of a dolichol (DCHOL) residue to form dolichyl phosphate (DOLP) in the ER membrane (Fernandez et al. 2002). DOLP is an important substrate in the synthesis of N- and O-glycosylated proteins and GPI anchors. Defects in DOLK cause congenital disorder of glycosylation type 1m (DOLK-CDG, CDG1m, also known as dolichol kinase deficiency; MIM:610768), a severe multisystem disorder characterised by under-glycosylated serum glycoproteins. This disorder has a very severe phenotype and death can occur in early life (Kranz et al. 2007). Mutations that can cause DOLK-CDG are C99S, Y441S, H408D, W304C and M1I (Kranz et al. 2007, Lefeber et al. 2011).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
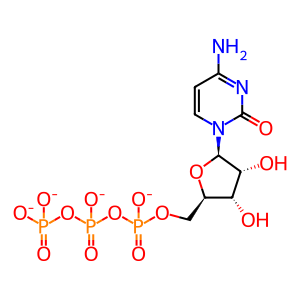
CTP [cytosol]
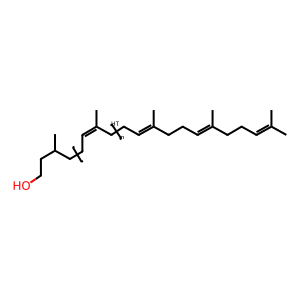
DCHOL [integral component of cytoplasmic side of endoplasmic reticulum membrane]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-4755600
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
CTP(4-)
dolichol
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-4755600