Reaction: Defective MGAT2 does not transfer GlcNAc to N-glycans
- in pathway: Defective MGAT2 causes CDG-2a
Alpha-1,6-mannosyl-glycoprotein 2-beta-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase (MGAT2) normally catalyses the transfer of a GlcNAc moiety onto the alpha,1,6 mannose of an alpha,1,4 branch of oligomannose N-glycans to form complex N-glycans (Tan et al. 1995). Defects in MGAT2 are associated with congenital disorder of glycosylation type IIa (MGAT2-CDG, CDG-2a; MIM:212066), a multisystem disorder caused by a defect in glycoprotein biosynthesis and characterised by under-glycosylated serum glycoproteins. Mutations that can cause MGAT2-CDG are S290F, H262R, C339*, N318D and K237N (Tan et al. 1996, Cormier-Daire et al. 2000, Alkuraya 2010, Alazami et al. 2012).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
UDP-GlcNAc [Golgi lumen]
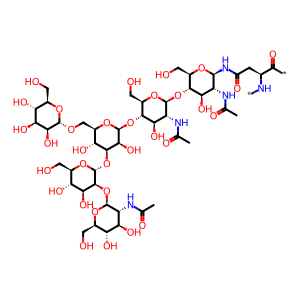
(GlcNAc)3 (Man)3 (Asn)1 [Golgi lumen]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-4793955
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
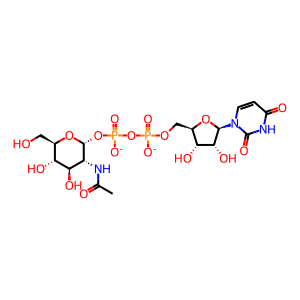
UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosamine(2-)
N(4)-{beta-D-GlcNAc-(1->2)-alpha-D-Man-(1->3)-[alpha-D-Man-(1->6)]-beta-D-Man-(1->4)-beta-D-GlcNAc-(1->4)-beta-D-GlcNAc}-Asn residue
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-4793955