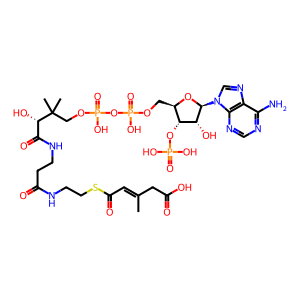
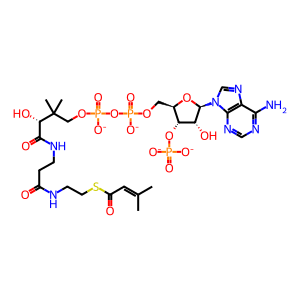
Reaction: beta-methylglutaconyl-CoA + ADP + orthophosphate + H2O <=> beta-methylcrotonyl-CoA + ATP + CO2 [MCCA]
- in pathway: Branched-chain amino acid catabolism
Methylcrotonyl CoA carboxylase (MCCA) catalyzes the reversible reaction of beta-methylglutaconyl-CoA, ADP, orthophosphate, and H2O to form beta-methylcrotonyl-CoA, ATP, and CO2. Active MCCA is composed of two polypeptides, MCCA1 and MCCA2 (Baumgartner et al. 2001; Holzinger et al. 2001). The enzyme has been purified from fibroblast mitochondria. By analogy to the more thoroughly studied bovine homologue, MCCA is thought to be a hexamer of six MCCA1:MCCA2 dimers, and the MCCA1 polypeptides are thought to have biotin moieties covalently bound to a lysine residue at position 681 in the polypeptide chain. Mitochondrial import of MCCA1 and 2 is associated with removal of aminoterminal mitochondrial targeting sequences but the exact lengths of these sequences have not been determined.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
bMC-CoA [mitochondrial matrix]
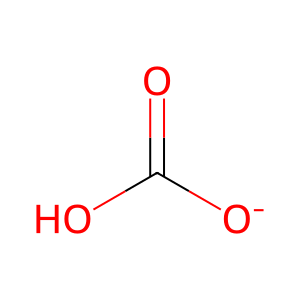
HCO3- [mitochondrial matrix]
ATP [mitochondrial matrix]
Pi [mitochondrial matrix]
ADP [mitochondrial matrix]
bMC-CoA [mitochondrial matrix]
H2O [mitochondrial matrix]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-508308
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
hydrogenphosphate
ADP(3-)
trans-3-methylglutaconyl-CoA
water
Reaction output - small molecules:
3-methylbut-2-enoyl-CoA(4-)
hydrogencarbonate
ATP(4-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-508308