Reaction: SUMO-CRABP2 binds atRA
- in pathway: Signaling by Retinoic Acid
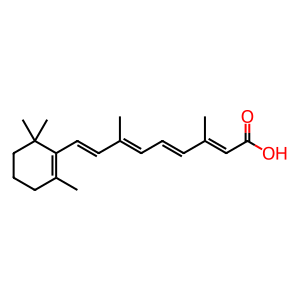
Cellular retinoic acid-binding protein 2 (CRABP2) is a cytosolic, lipid-binding protein thought to bind its natural ligand, all-trans-retinoic acid (atRA) and mediate its delivery to retinoic acid receptors (RARs) within the nucleus (Kleywegt et al. 1994). CRABP2 forms a beta-barrel structure within which a hydrophobic ligand can be accommodated. Once atRA binds to CRABP2, the resulting complex translocates to the nucleus (Budhu & Noy 2002). A ligand activated nuclear-localisation signal appears to be critical for nuclear localisation (Sessler & Noy 2005). Sumoylation of CRABPs is also essential for atRA-induced dissociation of CRABPs from the ER membrane. For CRABP2, the site K102 is sumoylated (Majumdar et al. 2011).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
atRA [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-5334827
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
all-trans-retinoic acid
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-5334827