Reaction: GGTs hydrolyse glutamate from AFXBO-SG, AFNBO-SG
- in pathway: Aflatoxin activation and detoxification
To be excreted in urine, glutathione conjugates undergo several hydrolysis steps to form mercapturic acids which are readily excreted. The first step is the hydrolysis of a gamma-glutamyl residue from the conjugate catalysed by gamma-glutamyltransferases (GGTs). These are membrane-bound, heterodimeric enzymes composed of light and heavy peptide chains. GGT1 and 2 are well characterised while GGT3P, 5, 6 and 7 are putative transferases. Extracellular glutathione or its conjugates can be hydrolysed to give cysteinylglycine (CG, or CG conjugates) and free glutamate (L-Glu) (Heisterkamp et al. 2008, Tate & Ross 1977, Pawlak et al. 1989).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
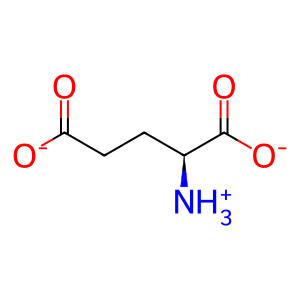
L-Glu [extracellular region]
H2O [extracellular region]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-5433072
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
Reaction output - small molecules:
L-glutamate(1-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-5433072