Reaction: ACSL3,4 ligate CoA to AA to form AA-CoA
- in pathway: Synthesis of very long-chain fatty acyl-CoAs
Acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 4 (ACSL4) associated with the endoplasmic reticulum membrane catalyses the conjugation of arachidonate (AA) with CoA to form arachidonyl-CoA (AA-CoA) (Longo et al. 2003, Meloni et al. 2003). By similarity, ACSL3 can also preferentially conjugate CoA on to AA (Yao & Ye 2008). These enzymes are involved in the activation of long-chain fatty acids for both synthesis of cellular lipids, and degradation via beta-oxidation.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
PPi [cytosol]
H2O [cytosol]
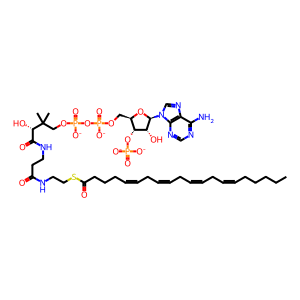
AA-CoA [cytosol]
AMP [cytosol]
ATP [cytosol]
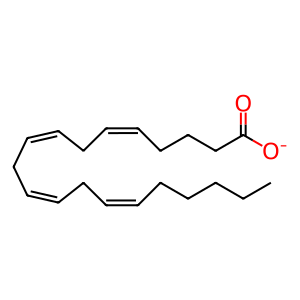
AA [cytosol]
CoA-SH [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-548843
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
ATP(4-)
arachidonate
coenzyme A(4-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
diphosphate(3-)
water
arachidonoyl-CoA(4-)
adenosine 5'-monophosphate(2-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-548843