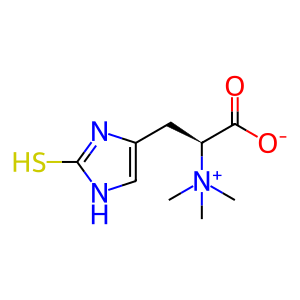
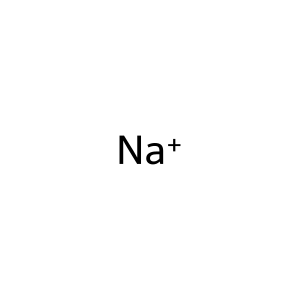Reaction: SLC22A4 cotransports ERGT, Na+ from extracellular region to cytosol
- in pathway: Organic cation transport
The human gene SLC22A4 encodes the ergothioneine transporter (ETT). It was originally discovered as an organic cation/carnitine transporter (OCTN1) (Tamai et al. 1997) but its main substrate is not carnitine. It is widely expressed and transports ergothioneine more than 100 times more efficiently than tetraethylammonium and carnitine (Grundemann et al. 2005), leading to the name change from OCTN1 to ETT. Defects in SLC22A4 could be implicated in rheumatoid arthritis (RA; MIM:180300), an inflammatory disease with autoimmune features and a complex genetic component (Tokuhiro et al. 2003, Yamada et al. 2004). An intronic SNP (slc2F2) in intron 1, consists of a susceptible T allele and a nonsusceptible C allele. The runt-related transcription factor 1 (RUNX1) has a suppressive effect on SLC22A4 expression and this suppression appears to be stronger with the susceptible T allele of SLC22A4 than with the nonsusceptible C allele, leading to a lower expression of SLC22A4 (Tokuhiro et al. 2003).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
Na+ [cytosol]
ERGT [cytosol]
ERGT [extracellular region]
Na+ [extracellular region]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-549241
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
ergothioneine
sodium(1+)
Reaction output - small molecules:
sodium(1+)
ergothioneine
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-549241