Reaction: Defective CYP24A1 does not 24-hydroxylate CALTOL
- in pathway: Defective CYP24A1 causes HCAI
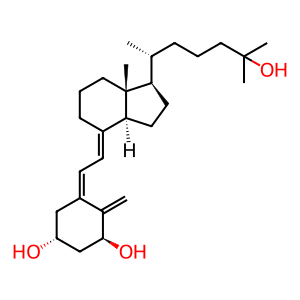
Catabolic inactivation of the active, hormonal form of vitamin D3 (calcitriol, CALTOL, 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3) is initially carried out by 24-hydroxylation, mediated by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 24-hydroxylase (CYP24A1). The product formed is eventually transformed to calcitroic acid, the major water-soluble metabolite that can be excreted in bile. Defects in CYP24A1 can cause hypercalcemia infantile (HCAI; MIM:143880), a disorder characterised by abnormally high level of calcium in the blood, failure to thrive, vomiting, dehydration, and nephrocalcinosis. CYP24A1 mutations causing HCAI include C477Lfs*14, E143del, E151*, R159Q, R396W and E322K (Schlingmann et al. 2011).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
O2 [mitochondrial matrix]
H+ [mitochondrial matrix]
CTL [mitochondrial matrix]
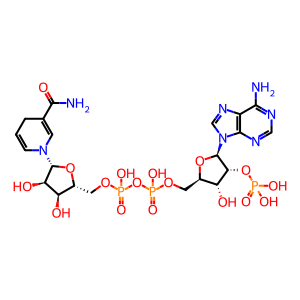
NADPH [mitochondrial matrix]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-5602004
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
dioxygen
hydron
calcitriol
NADPH
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-5602004