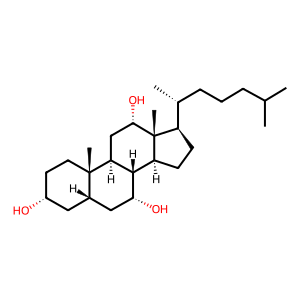
Reaction: CYP27A1 does not 27-hydroxylate 5bCHOL3a,7a,12a-triol
- in pathway: Defective CYP27A1 causes CTX
CYP27A1, a mitochondrial matrix sterol hydroxylase, catalyses the 27-hydroxylation of side-chains of sterol intermediates (Cali et al. 1991). In the bile acid synthesis pathway, CYP27A1 catalyses the first step in the oxidation of the side chain of sterol intermediates such as 5beta-cholestan-3alpha, 7alpha, 12alpha-triol (5bCHOL3a,7a,12a-triol) to form 5beta-cholestan-3alpha, 7alpha, 12alpha, 27-tetrol (5bCHOL3a,7a,12a, 27-tetrol) (Pikuleva et al. 1998). Defects in CYP27A1 can cause Cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis (CTX; MIM:213700), a rare sterol storage disorder characterised by progressive neurologic dysfunction, premature atherosclerosis and cataracts (Cali et al. 1991b). Mutations that have a relatively high frequency in some ethnic groups are T339M (Dutch) (Guyant-Marechal et al. 2005), R474(Q-W) (Japanese) (Kim et al. 1994) and A216P (Italian) (Garuti et al. 1996).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
O2 [mitochondrial matrix]
5bCHOL3a,7a,12a-triol [mitochondrial matrix]
H+ [mitochondrial matrix]
NADPH [mitochondrial matrix]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-5602170
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
dioxygen
5beta-cholestane-3alpha,7alpha,12alpha-triol
hydron
NADPH
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-5602170