Reaction: Defective CYP2U1 does not omega-hydroxylate ARA
- in pathway: Defective CYP2U1 causes SPG56
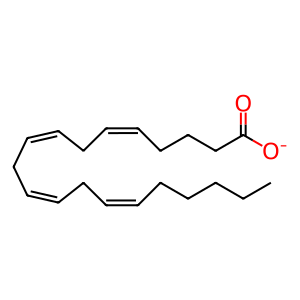
Cytochrome P450 2U1 (CYP2U1) catalyses the hydroxylation of arachidonic acid, docosahexaenoic acid and other long chain fatty acids, generating bioactive eicosanoid derivatives which may play an important physiological role in fatty acid signaling processes. Defects in CYP2U1 can cause Spastic paraplegia 56, autosomal recessive (SPG56; MIM:615030), a neurodegenerative disorder characterised by a slow, gradual, progressive weakness and spasticity of the lower limbs (Tesson et al. 2012, Fink 2013). CYP2U1 mutations that cause SPG56 are D316V, E380G, C262R, R488W and L21Wfs*19 (Tesson et al. 2012).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
O2 [endoplasmic reticulum lumen]
H+ [endoplasmic reticulum lumen]
AA [endoplasmic reticulum lumen]
NADPH [endoplasmic reticulum lumen]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-5602242
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
dioxygen
hydron
arachidonate
NADPH
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-5602242