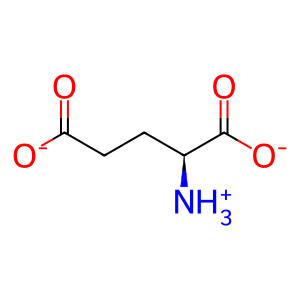
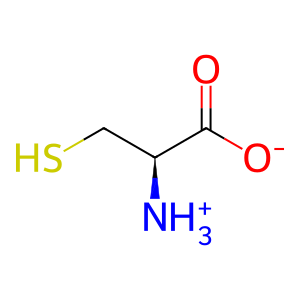
Reaction: Defective GCLC does not ligate L-Glu to L-Cys
- in pathway: Defective GCLC causes HAGGSD
Gamma-glutamylcysteine ligase (GCL) catalyses the first and rate-limiting step in GSH biosynthesis. GCL is a heterodimer of a catalytic heavy chain (GCLC) and a regulatory light chain (GCLM). Defects in the catalytic GCLC can cause hemolytic anemia due to gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase deficiency (HAGGSD; MIM:230450), a disease characterised by hemolytic anemia, glutathione deficiency, myopathy, late-onset spinocerebellar degeneration, and peripheral neuropathy. Mutations causing HAGGSD are H370L, P185L and R127C (Beutler et al. 1999, Ristoff et al. 2000, Hamilton et al. 2003).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
L-Glu [cytosol]
L-Cys [cytosol]
ATP [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-5602892
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
L-glutamate(1-)
L-cysteine zwitterion
ATP(4-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-5602892