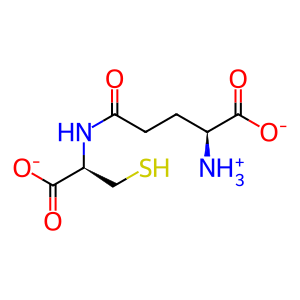
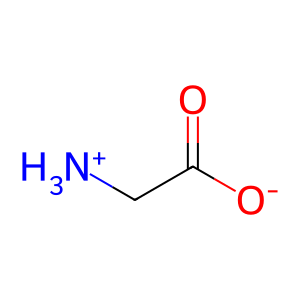
Reaction: Defective GSS does not synthesize GSH
- in pathway: Defective GSS causes GSS deficiency
In the second step in glutathione formation, gamma-glutamylcysteine (gGluCys) ligates with glycine (Gly) to form glutathione (GSH), catalysed by glutathione synthetase (GSS), a homodimeric enzyme present in the cytosol. Defects in GSS can cause glutathione synthetase deficiency (GSSD aka 5-oxoprolinase deficiency, MIM:266130), a severe, autosomal recessive disorder characterised by an increased rate of haemolysis, 5-oxoprolinuria and defective function of the central nervous system. In this condition, decreased levels of cellular glutathione result in overstimulation of gamma-glutamylcysteine synthesis and its subsequent conversion to 5-oxoproline. Mutations causing severe GSSD include R164Q, R267W, R283C, R125C and P314L (Shi et al. 1996).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
gGluCys [cytosol]
ATP [cytosol]
Gly [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-5602901
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
L-gamma-glutamyl-L-cysteinate(1-)
ATP(4-)
glycine zwitterion
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-5602901