Reaction: Defective MAT1A does not transfer Ado from ATP to L-Met
- in pathway: Defective MAT1A causes MATD
S-adenosylmethionine (AdoMet, SAM) is an important methyl donor in most transmethylation reactions. S-adenosylmethionine synthase isoform type-1 (MAT1A) catalyses the formation of AdoMet from methionine and ATP. Defects in MAT1A can cause methionine adenosyltransferase deficiency (MATD; MIM:250850), an inborn error of metabolism resulting in hypermethioninemia. In this condition, methionine accumulates because its conversion to AdoMet is impaired. Frameshift mutations causing complete loss of MAT1A function are K181Vfs*5, H277Afs*75 and V348Gfs*3 (Hazelwood et al. 1998, Chamberlin et al. 1996).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
H2O [cytosol]
ATP [cytosol]
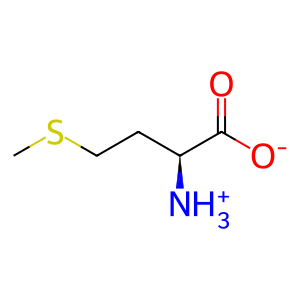
L-Met [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-5603087
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
ATP(4-)
L-methionine zwitterion
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-5603087