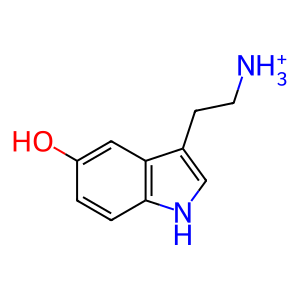
Reaction: Defective MAOA does not oxidatively deaminate 5HT
- in pathway: Defective MAOA causes BRUNS
Amine oxidase (flavin-containing) A (MAOA) catalyses the oxidative deamination of biogenic and dietary amines, the regulation of which is critical for mental state homeostasis. MAOA, located on the mitochondrial outer membrane and requiring FAD as cofactor, preferentially oxidises biogenic amines such as 5-hydroxytryptamine (5HT), dopamine, noradrenaline and adrenaline. Defects in MAOA can cause Brunner syndrome (BRUNS; MIM:300615), a form of X-linked non-dysmorphic mild mental retardation. Male patients are affected by mild mental retardation and exhibit abnormal behaviour, including impulsive aggression. A mutation that causes BRUNS is Q296* (Brunner et al. 1993).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
H2O [cytosol]
5HT [cytosol]
O2 [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-5603108
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
serotonin(1+)
dioxygen
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-5603108