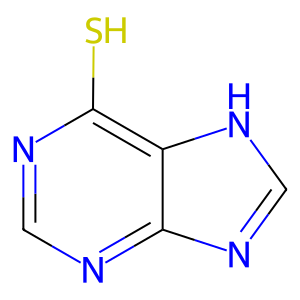
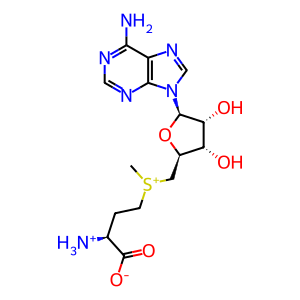
Reaction: TPMT does not transfer CH3 from AdoMet to 6MP
- in pathway: Defective TPMT causes TPMT deficiency
6-mercaptopurine (6MP) is used in the treatment of inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. 6MP and its thioguanine nucleotide metabolites are principally inactivated by thiopurine methyltransferase (TPMT)-catalysed S-methylation. Defects in TPMT can cause thiopurine S-methyltransferase deficiency (TPMT deficiency; MIM:610460). Patients with intermediate or no TPMT activity are at risk of toxicity after receiving standard doses of thiopurine drugs. Inter-individual differences in response to these drugs are largely determined by genetic variation at the TPMT locus. Variants that cause complete or almost complete loss of function are A154T and Y240C (variants TPMT*3B and 3C, together called TPMT*3A), A80P (TPMT*2) and A167G (TPMT*23) (Szumlanski et al. 1996, Tai et al. 1997, Lindquist et al. 2007).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
6MP [cytosol]
AdoMet [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-5603379
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
purine-6-thiol
S-adenosyl-L-methionine zwitterion
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-5603379