Reaction: TRAF6 oligomer autoubiquitinates
- in pathway: CLEC7A (Dectin-1) signaling
TRAF6 possesses ubiquitin ligase activity and undergoes K-63-linked auto-ubiquitination after its oligomerization. In the first step, ubiquitin is activated by an E1 ubiquitin activating enzyme. The activated ubiquitin is transferred to a E2 conjugating enzyme (a heterodimer of proteins Ubc13 and Uev1A also known as TRIKA1 (TRAF6-regulated IKK activator 1)) forming the E2-Ub thioester. Finally, in the presence of ubiquitin-protein ligase E3 (TRAF6, a RING-domain E3), ubiquitin is attached to the target protein (TRAF6 on residue Lysine 124) through an isopeptide bond between the C-terminus of ubiquitin and the epsilon-amino group of a lysine residue in the target protein (Deng et al. 2000, Lamothe et al. 2007). In contrast to K-48-linked ubiquitination that leads to the proteosomal degradation of the target protein, K-63-linked polyubiquitin chains act as a scaffold to assemble protein kinase complexes and mediate their activation through proteosome-independent mechanisms. This K63 polyubiquitinated TRAF6 activates the TAK1 kinase complex.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
PPi [cytosol]
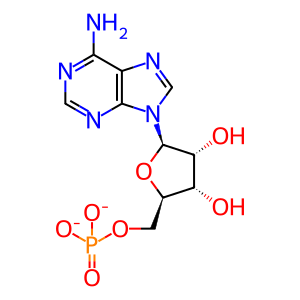
AMP [cytosol]
ATP [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-5607756
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
ATP(4-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
diphosphate(3-)
adenosine 5'-monophosphate(2-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-5607756