Reaction: Defective PGM1 does not isomerise G6P to G1P
- in pathway: Defective PGM1 causes PGM1-CDG
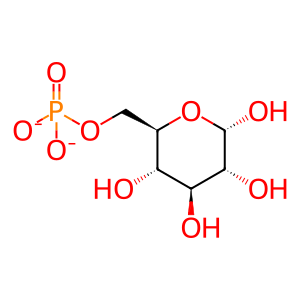
Cytosolic phosphoglucomutase (PGM) catalyses the reversible conversion of glucose 6-phosphate (G6P) to glucose 1-phosphate (G1P), both precursor intermediates in glucose metabolism and protein glycosylation processes. Defects in PGM1 can cause Congenital disorder of glycosylation 1t (CDG1t, now known as PGM1-CDG; MIM:614921), a broad spectrum disorder characterised by under-glycosylated serum glycoproteins (Timal et al. 2012, Tegtmeyer et al. 2014). CDGs result in a wide variety of clinical features such as defects in nervous system development, psychomotor retardation, dysmorphic features, hypotonia, coagulation disorders, and immunodeficiency. Mutations that cause almost complete loss of PGM1 activity include T115A, N38Y, D62H, D263Y and R221Vfs*13 (Tegtmeyer et al. 2014).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
G6P [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-5609939
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
alpha-D-glucose 6-phosphate(2-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-5609939