Reaction: Defective GALT does not transfer UMP to Gal1P
- in pathway: Defective GALT can cause GALCT
Galactose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase (GALT) is one of the enzymes involved in galactose metabolism in the Leloir pathway. GALT catalyses the transfer of uridine monophosphate (UMP) from UDP-glucose (UDP-Glc) to galactose-1-phosphate (Gal1P) to form UDP-galactose (UDP-Gal). Defects in GALT can cause Galactosemia (GALCT; MIM:230400), an autosomal recessive disorder of galactose metabolism presenting in neonatals that causes jaundice, cataracts, and mental retardation. Q188R, K285N are the most common mutations in US Caucasians (Reichardt et al. 1991, Elsas et al. 1994). S135L is the most common mutation of the American black population (Lai et al. 1996). Protein misfolding is likely to be the underlying molecular cause in the majority of cases (McCorvie et al. 2013).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
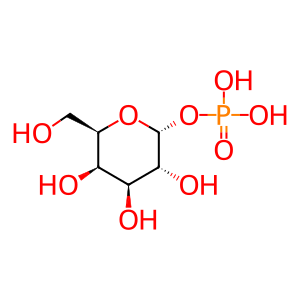
Gal1P [cytosol]
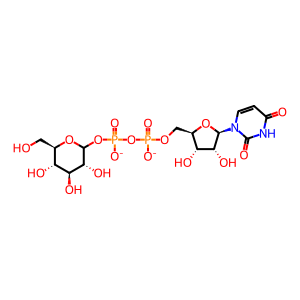
UDP-D-glucose(2-) [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-5610038
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
alpha-D-galactose 1-phosphate
UDP-D-glucose(2-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-5610038