Reaction: Defective POMT2 does not transfer Man from Dol-P-Man to DAG1
- in pathway: Defective POMT2 causes MDDGA2, MDDGB2 and MDDGC2
Co expression of both protein O mannosyl transferases 1 and 2 (POMT1 and POMT2; CAZy family GT39) is necessary for enzyme activity, that is mediating the transfer of mannosyl residues to the hydroxyl group of serine or threonine residues of proteins such as alpha dystroglycan (DAG1; MIM:128239). DAG1 is a cell surface protein that plays an important role in the assembly of the extracellular matrix in muscle, brain, and peripheral nerves by linking the basal lamina to cytoskeletal proteins. Defects in POMT2 (MIM:607439) results in defective glycosylation of DAG1 and can cause severe congenital muscular dystrophy dystroglycanopathies ranging from a severe type A, MDDGA2 (brain and eye abnormalities; MIM:613150), through a less severe type B, MDDGB2 (congenital form with mental retardation; MIM:613156) to a milder type C, MDDGC2 (limb girdle form; MIM:603158) (Bertini et al. 2011, Wells 2013). Several mutations are known (MIM:607439), and mutations causing the severest type A2 form include R638*, T433* (van Reeuwijk et al. 2005), I444_N445insLLWQ, Y666C (Yanagisawa et al. 2009), V373F and I198N (Godfrey et al. 2007).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
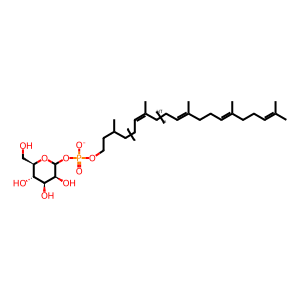
DOLP-Man [integral component of cytoplasmic side of endoplasmic reticulum membrane]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-5615556
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
dolichyl D-mannosyl phosphate(1-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-5615556