Reaction: Retinoic acid activates HOXA4 chromatin
As inferred from mouse embryos, retinoic acid initially activates expression of the HOXA4 gene in rhombomere 7 (r7) by binding RARB or RARA in dimeric RAR:RXR complexes located at retinoic acid response elements (RAREs) in the 5' flanking region of the HOXA4 promoter (also observed in human teratocarcinoma cells in Doerksen et al. 1996, Sessa et al. 2007), correlating dissociation of corepressors and recruitment of coactivators. In mouse embryos Hoxa4 itself maintains later expression in an autoregulatory loop.
In human fibroblasts (Lan et al. 2007) and teratocarcinoma cells (Sessa et al 2007) activation of HOXA4 chromatin is accompanied by loss of methylation at lysine-27 of histone H3 (H3K27me3) and gain of H3K4me3. The polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2), which binds H3K27me3, is also reduced at active HOXA4 chromatin (Lan et al. 2007, Sessa et al. 2007).
In human fibroblasts (Lan et al. 2007) and teratocarcinoma cells (Sessa et al 2007) activation of HOXA4 chromatin is accompanied by loss of methylation at lysine-27 of histone H3 (H3K27me3) and gain of H3K4me3. The polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2), which binds H3K27me3, is also reduced at active HOXA4 chromatin (Lan et al. 2007, Sessa et al. 2007).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
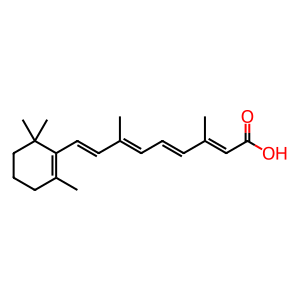
atRA [nucleoplasm]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-5617862
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
all-trans-retinoic acid
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-5617862