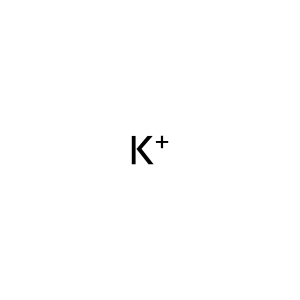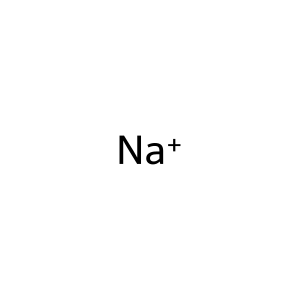Reaction: Defective SLC12A1 does not cotransport Na+, K+, 2Cl- from extracellular region to cytosol
- in pathway: Defective SLC12A1 causes Bartter syndrome 1 (BS1)
The solute carrier family 12 member 1 (SLC12A1, NKCC2) is a kidney-specific, membrane-bound protein that cotransports two Cl- ions electroneutrally into cells with a Na+ ion and a K+ ion and plays a vital role in the regulation of ionic balance and cell volume. Defects in SLC12A1 can cause Bartter’s syndrome (BS1; MIM:601678), an autosomal-recessive disease salt-wasting disorder characterised by renal tubular hypokalaemia, metabolic alkalosis and hypercalciuria. Clinical features present in infancy and include muscle weakness, anorexia, polydipsia, polyuria, failure to thrive and mental and growth retardation.
Loss-of-function defects in SLC12A1 that cause BS1 include D648N, V272F (Simon et al. 1996), R302Q, G319R (Vargas-Poussou et al. 1998), W625X (Kurtz et al. 1997) and Y998* (Vargas-Poussou et al. 1998).
Loss-of-function defects in SLC12A1 that cause BS1 include D648N, V272F (Simon et al. 1996), R302Q, G319R (Vargas-Poussou et al. 1998), W625X (Kurtz et al. 1997) and Y998* (Vargas-Poussou et al. 1998).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
K+ [extracellular region]
Cl- [extracellular region]
Na+ [extracellular region]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-5623588
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
potassium(1+)
chloride
sodium(1+)
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-5623588