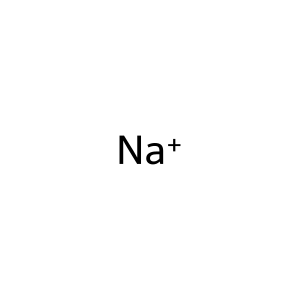Reaction: Defective SLC12A3 does not cotransport Cl-, Na+ from extracellular region to cytosol
- in pathway: Defective SLC12A3 causes Gitelman syndrome (GS)
The SLC12A3 gene encodes for the Thiazide-sensitive sodium-chloride cotransporter (TSC). TSC mediates sodium and chloride removal from the distal convoluted tubule of the kidney. Defects in SLC12A3 are the cause of Gitelman syndrome (GS aka familial hypokalemic hypomagnesemia; MIM:263800). GS is an autosomal recessive disorder characterised by hypokalemic metabolic alkalosis, hypomagnesemia, and hypocalciuria. Patients can present with periods of muscular weakness and tetany, usually accompanied by abdominal pain, vomiting and fever. GS has overlapping features with Bartter syndrome (caused by defects in SLC12A1). Mutations in SLC12A3 that can cause GS include L850P, L272P, G741R, T392I and E121D (Simon et al. 1996, Glaudemans et al. 2012). The most common mutation in Asian GS patients is T60M (Yang et al. 2013).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
Cl- [extracellular region]
Na+ [extracellular region]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-5623705
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
chloride
sodium(1+)
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-5623705