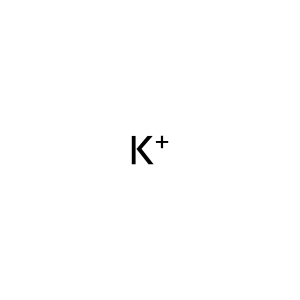Reaction: Defective SLC12A6 does not cotransport K+, Cl- from cytosol to extracellular region
- in pathway: Defective SLC12A6 causes agenesis of the corpus callosum, with peripheral neuropathy (ACCPN)
K+/Cl- cotransport is implicated not only in regulatory volume decrease, but also in transepithelial salt absorption, renal K+ secretion, myocardial K+ loss during ischemia and regulation of neuronal Cl- concentration. Four genes (SLC12A4-7) encode the K+/Cl- cotransporters KCC1-4 respectively. Cotransport of K+ and Cl- is electroneutral with a 1:1 stoichiometry. These cotransporters function as homomultimers or heteromultimers with other K+/Cl- cotransporters. SLC12A6 encodes KCC3 which is highly expressed in heart, brain, spinal cord, kidney, muscle, pancreas and placenta. Defects in SLC12A6 are a cause of agenesis of the corpus callosum with peripheral neuropathy (ACCPN; MIM:218000), a autosomal recessive disease characterised by severe progressive sensorimotor neuropathy, mental retardation, dysmorphic features and variable degree of agenesis of the corpus callosum.
Mutations in SLC12A6 that can cause ACCPN include T813fs*813, F529fs*532, R1011*, R675* and R1134* (Howard et al. 2002, Salin-Cantegrel et al. 2011).
Mutations in SLC12A6 that can cause ACCPN include T813fs*813, F529fs*532, R1011*, R675* and R1134* (Howard et al. 2002, Salin-Cantegrel et al. 2011).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
K+ [cytosol]
Cl- [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-5623806
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
potassium(1+)
chloride
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-5623806