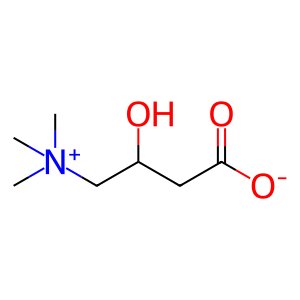
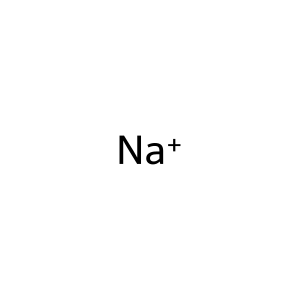Reaction: Defective SLC22A5 does not cotransport CAR, Na+ from extracellular region to cytosol
SLC22A5 encodes the organic cation/carnitine transporter 2 (OCTN2). It is a sodium-dependent, high affinity carnitine cotransporter which maintain systemic and tissue concentrations of carnitine. Carnitine is essential for beta-oxidation of long-chain fatty acids to produce ATP. SLC22A5 is strongly expressed in the kidney, skeletal muscle, heart and placenta. Defects in SLC22A5 are the cause of systemic primary carnitine deficiency (CDSP; MIM:212140), an autosomal recessive disorder of fatty-acid oxidation caused by defective carnitine transport resulting in cardiac, skeletal, or metabolic symptoms. If diagnosed early, all clinical symptoms can be completely reversed with a carnitine supplement. However, if left untreated, patients will develop lethal heart failure. Mutations that can cause CDSP include W132*, P478L, R169Q, R169W, R254* and G15W (Nezu et al. 1999, Tang et al. 1999, Burwinkel et al. 1999, Wang et al. 2000, Tang et al. 2002, El-Hattab et al. 2010).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
CAR [extracellular region]
Na+ [extracellular region]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-5625674
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
carnitine
sodium(1+)
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-5625674