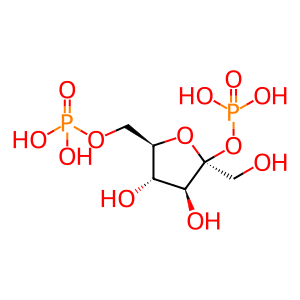
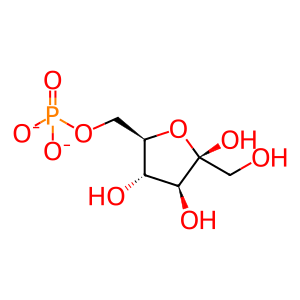
Reaction: TIGAR converts D-fructose-2,6-bisphosphate to D-fructose 6-phosphate
- in pathway: TP53 Regulates Metabolic Genes
TIGAR shares similarity with PGMs (phosphoglycerate mutases), especially PFK2 (6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase). TIGAR possesses only the bisphosphatase domain and converts D-fructose 2,6-bisphosphate into D-fructose 6-phosphate (Bensaad et al. 2006). Reduction of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate levels correlates with decrease in glycolytic rates, which makes cells more sensitive to apoptotic stimuli (Vander Heiden et al. 2001). Alternatively, fructose 6-phosphate can be isomerized to glucose 6-phosphate, which is diverted to the pentose phosphate pathway, which can have an anti-apoptotic effect (Boada et al. 2000, Perez et al. 2000). In the pentose phosphate pathway, oxidized glutathione is reduced, and this reduced glutathione can then be used by glutathione peroxidase to remove hydrogen peroxide, thereby protecting cells from the oxidative stress (Kletzien et al. 1994, Fico et al. 2004, Tian et al. 1999). Indeed, expression of TIGAR increases reduced glutathione to oxidized glutathione ratio and lowers ROS (reactive oxygen species) levels in cells (Bensaad et al. 2006, Lee et al. 2014).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
Pi [cytosol]
Fru(6)P [cytosol]
H2O [cytosol]
D-Fructose 2,6-bisphosphate [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-5628905
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
beta-D-fructofuranose 2,6-bisphosphate
Reaction output - small molecules:
hydrogenphosphate
beta-D-fructofuranose 6-phosphate(2-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-5628905