Reaction: Defective ALG14 does not transfer GlcNAc from UDP-GlcNAc to GlcNAcDOLP
- in pathway: Defective ALG14 causes ALG14-CMS
UDP-N-acetylglucosamine transferase subunit ALG14 homolog (ALG14) forms a complex with ALG13 protein and is required for the addition of the second N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) to the lipid linked oligosaccharide (LLO) intermediate (GlcNAcDOLDP) (Gao et al. 2005). Defects in ALG14 can cause congenital myasthenic syndrome (ALG14-CMS), which is due to a defect in neuromuscular signal transmission (Cossins et al. 2013). The most commonly affected muscles include proximal limb muscles. Mutations causing ALG14-CMS include p.P65L and p.R104* (Cossins et al. 2013).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
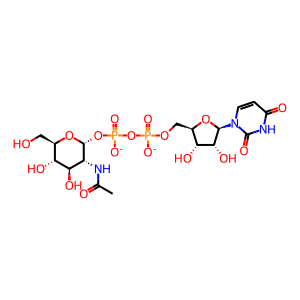
UDP-GlcNAc [cytosol]
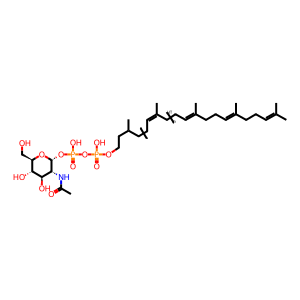
GlcNAcDOLDP [integral component of cytoplasmic side of endoplasmic reticulum membrane]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-5633241
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosamine(2-)
N-acetyl-D-glucosaminyldiphosphodolichol
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-5633241