Reaction: Defective SLC35A2 does not exchange UDP-Gal, UDP-GalNAc for UMP
The human gene SLC35A2 encodes the UDP-galactose transporter. It is located on the Golgi membrane and mediates the antiport of UDP-Gal into the Golgi lumen in exchange for UMP. Nucleotide sugars such as UDP-Gal are used in protein glycosylation in the Golgi lumen. This transporter is also known to transport UDP-N-acetylgalactosamine (UDP-GalNAc) by the same antiport mechanism. Defects in SLC35A2 limit Golgi-localised pools of UDP-Gal, resulting in truncated beta-GlcNAc-terminated N-glycans and alpha-GalNAc-terminated O-glycans. Defects in SLC35A2 can cause congenital disorder of glycosylation 2M (CDG2M; MIM:300896), a disorder characterised by developmental delay, hypotonia, ocular defects and brain malformations. Congenital disorders of glycosylation (CDGs) are generally characterised by under-glycosylated serum glycoproteins and a wide spectrum of clinical features. Mutations in SLC25A2 causing CDG2M are G8Sfs*9, V331I and M1? (Ng et al. 2013). Defects in SLC35A2 can also cause early infantile epileptic encephalopathy 22 (EIEE22; MIM:300896), a severe form of epilepsy characterised by by frequent tonic seizures or spasms beginning in infancy and accompanied by developmental problems. Mutations in SLC35A2 causing EIEE22 are Y145Pfs*76 and F324Lfs*25 (Kodera et al. 2013).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
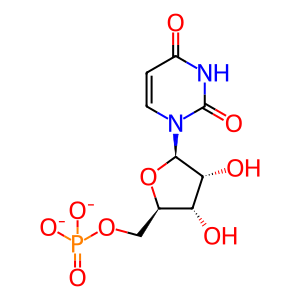
UMP [Golgi lumen]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-5652099
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
uridine 5'-monophosphate(2-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-5652099