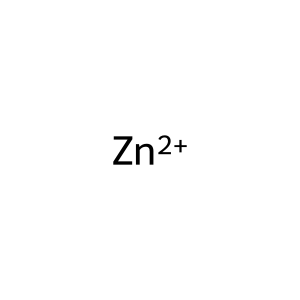Reaction: Defective SLC39A4 does not transport Zn2+ from extracellular region to cytosol
SLC39A4 encodes the human zinc transporter hZIP4 which plays an important role in cellular zinc homeostasis. Defects in SLC39A4 result in the inherited condition acrodermatitis enteropathica, zinc deficiency type (AEZ; MIM:201100), caused by the inability to absorb dietary zinc from the duodenum and jejunum. Clinical features include growth retardation, immune system dysfunction, severe dermatitis and mental disorders. Mutations casuing AEZ include G512W, L549del, G330D, P200L, G526R, R95C, 1223_1227del and 968_971del (Kury et al. 2002, Wang et al. 2003, Nakano et al. 2003, Schmitt et al. 2009).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
Zn2+ [extracellular region]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-5654125
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
zinc(2+)
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-5654125