Reaction: Defective SLC3A1 (in SLC7A9:SLC3A1) does not exchange L-Arg, CySS-, L-Lys for L-Leu
- in pathway: Defective SLC3A1 causes cystinuria (CSNU)
Neutral and basic amino acid transport protein rBAT (SLC3A1) and b(0,+)-type amino acid transporter 1 (SLC7A9) are linked by a disulfide bridge to form system b(0,+)-like activity in the high affinity transport of neutral and dibasic amino acids and cystine. The SLC7A9:SLC3A1 heterodimer mediates the electrogenic exchange of extracellular amino acids such as L-arginine (L-Arg) and L-lysine (L-lys) and cystine (CySS-, the oxidised form of L-cysteine) for intracellular neutral amino acids such as L-leucine (L-Leu). These solute carriers are mainly expressed in the kidney and small intestine where they remove dibasic amino acids and cystine from the renal tubular and intestinal lumen respectively. Defects in SLC3A1 (or SLC7A9) can cause cystinuria (CSNU; MIM:220100), an autosomal recessive disorder characterised by impaired epithelial cell transport of cystine and dibasic amino acids in the proximal renal tubule and GI tract. The build-up and low solubility of cystine causes the formation of calculi in the urinary tract, resulting in obstructive uropathy, pyelonephritis and in severe cases, renal failure. Cystinuria is subcategorized as type A (mutations on SLC3A1) and type B (mutations on SLC7A9). Mutations in SLC3A1 that can cause CSNU type A include M467T, M467K, R181Q, P615T, L678P and Y533N (Calonge et al. 2004, Barbosa et al. 2012).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
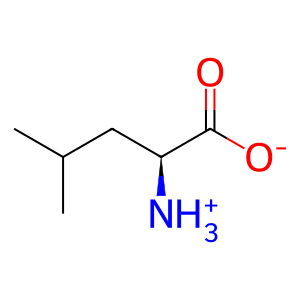
L-Leu [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-5655702
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
L-leucine zwitterion
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-5655702