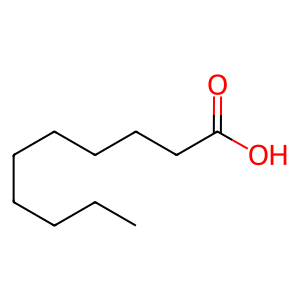
Reaction: OLAH hydrolyzes decanoyl-FASN dimer to DECA and FASN dimer
- in pathway: Fatty acyl-CoA biosynthesis
OLAH, a monomeric cytosolic thiolase, catalyzes the hydrolysis of FASN (fatty acid synthase) charged with decanoyl fatty acyl moieties to yield FASN and decanoate (DECA). OLAH expression is confined to the lactating mammary gland, and its catalytic activity enables the early termination of a portion of fatty acid biosynthesis to produce the medium chain-length fatty acids (annotated here as DECA) found in milk (Insull & Ahrens 1959; Breckenridge et al. 1969). OLAH is known only as an open reading frame identified in the human genome and as an mRNA observed in gene expression screening studies. Its biological properties are inferred from those of its well-studied rat ortholog (Libertini & Smith 1978; Mikkelsen et al. 1987).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
DECA [cytosol]
H2O [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-5655955
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
Reaction output - small molecules:
decanoic acid
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-5655955