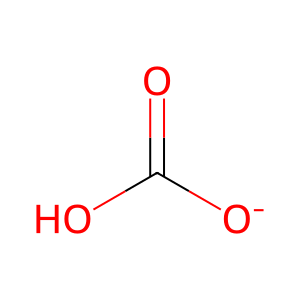
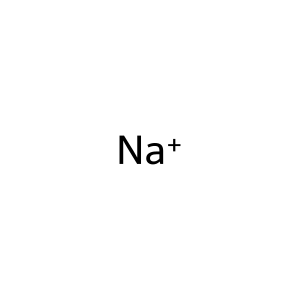Reaction: Defective SLC4A4 does not cotransport Na+ with 3HCO3-
- in pathway: Defective SLC4A4 causes renal tubular acidosis, proximal, with ocular abnormalities and mental retardation (pRTA-OA)
Members 4, 5, 7 and 9 of the SLC4A family couple the transport of bicarbonate (HCO3-) with sodium ions (Na+). SLC4A4 (aka NBCe1) is an electrogenic Na+/HCO3- cotransporter with a stoichiometry of 1:3. SLC4A4 is expressed in the kidney and pancreas, with lesser expression in many other tissues. Mutations in SLC4A4 can cause permanent isolated proximal renal tubular acidosis with ocular abnormalities and mental retardation (pRTA-OA), a rare autosomal recessive syndrome characterised by short stature, proximal renal tubular acidosis, mental retardation, bilateral glaucoma, cataracts and bandkeratopathy. pRTA results from the failure of the proximal tubular cells to reabsorb filtered HCO3- from urine, leading to urinary HCO3- wasting and subsequent acidemia. HCO3- also needs to move out of cells in the eye, thus failure to do so can affect ocular pressure homeostasis. Mutations causing pRTA-OA include Q29*, R298S, S427L, T485S, R510H, W516*, A799V and a 65bp-del (Igarashi et al. 1999, Dinour et al. 2004, Horita et al. 2005, Lo et al. 2011, Suzuki et al. 2010).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
HCO3- [cytosol]
Na+ [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-5656219
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
hydrogencarbonate
sodium(1+)
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-5656219