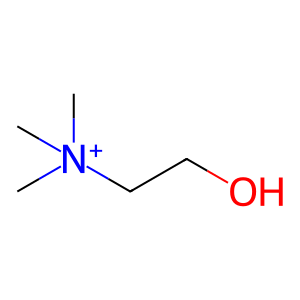
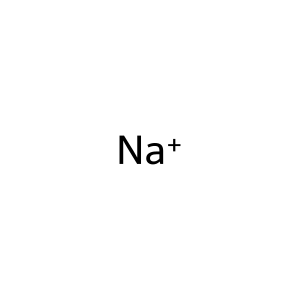Reaction: Defective SLC5A7 does not cotransport Cho, Cl-, Na+ from extracellular region to cytosol
The human SLC5A7 gene encodes a sodium- and chloride-dependent, high affinity choline transporter (CHT)
transports choline (Cho) from the extracellular space into neuronal cells. Cho uptake is the rate-limiting step in acetylcholine synthesis, aneurotransmitter released at the neuromuscular junction (NMJ). Defects in SLC5A7 can cause distal hereditary motor neuronopathy 7A (HMN7A; MIM:158580). Distal hereditary motor neuronopathies are a group of neuromuscular disorders caused by selective degeneration of motor neurons in the anterior horn of the spinal cord, without sensory deficit in the posterior horn. The clinical picture consists of a progressive distal muscle wasting and weakness in the legs without clinical sensory loss (Barwick et al. 2012). The c.1497delG change in the nucleotide sequence of SLC5A7 is predicted to result in a translational frameshift p.Lys499Asnfs*13 which can cause HMN7A (Barwick et al. 2012).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
Cl- [extracellular region]
Cho [extracellular region]
Na+ [extracellular region]
Cl- [extracellular region]
Cho [extracellular region]
Na+ [extracellular region]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-5658483
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
chloride
choline
sodium(1+)
chloride
choline
sodium(1+)
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-5658483