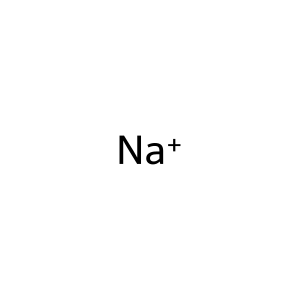Reaction: Defective SLC6A19 does not cotransport neutral amino acids, Na+ from extracellular region to cytosol
- in pathway: Defective SLC6A19 causes Hartnup disorder (HND)
SLC6A19 encodes the sodium-dependent neutral amino acid transporter B(0)AT1 and mediates the uptake of neutral amino acids across the plasma membrane accompanied by uptake of a sodium ion. The protein is abundantly expressed in the small intestine and kidney. Defects in SLC6A19 can cause Hartnup disorder (HND; MIM:234500), an autosomal recessive abnormality of renal and gastrointestinal neutral amino acid transport characterised by increased urinary and intestinal excretion of neutral amino acids. Symptoms include transient manifestations of rashes, cerebellar ataxia and psychotic behaviour. Mutations causing HND include D173N, R240*, V295Afs*57, S303L and I596Hfs*73 (Seow et al. 2004, Kleta et al. 2004, Cheon et al. 2010).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
Na+ [extracellular region]
Na+ [extracellular region]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-5659734
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
sodium(1+)
sodium(1+)
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-5659734