Reaction: Defective SLC7A9 (in SLC7A9:SLC3A1) does not exchange L-Arg, CySS-, L-Lys for L-Leu
- in pathway: Defective SLC7A9 causes cystinuria (CSNU)
SLC7A9 encodes the b(0,+)-type amino acid transporter 1 BAT1. As a heterodimer with SLC3A1 in the plasma membrane, SLC7A9 mediates the high affinity, sodium independent transport of cystine (CySS-, the oxidised form of L cysteine) and of dibasic amino acids in exchange for neutral amino acids and is thought to be responsible for the reabsorption of CySS- and dibasic amino acids in the kidney tubule (Schweikhard & Ziegler 2012). Defects in SLC7A9 (or SLC3A1) can cause cystinuria (CSNU; MIM:220100), an autosomal disorder characterised by impaired renal reabsorption of cystine and dibasic amino acids. The low solubility of cystine causes the formation of calculi in the urinary tract resulting in obstructive uropathy, pyelonephritis, and, rarely, renal failure. Cystinuria is subcategorised as type A (mutations on SLC3A1) and type B (mutations on SLC7A9). Mutations causing CSNU type B include V170M, G105R, R333W and Y232C (International Cystinuria Consortium 2001, Font-Llitjos et al. 2005).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
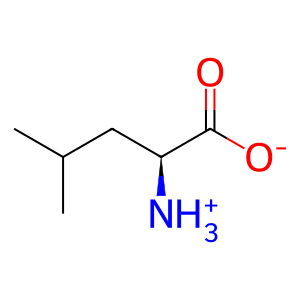
L-Leu [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-5660890
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
L-leucine zwitterion
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-5660890