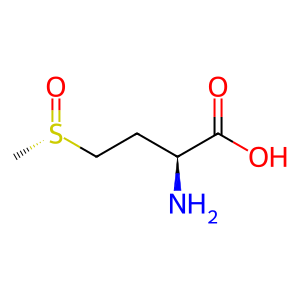
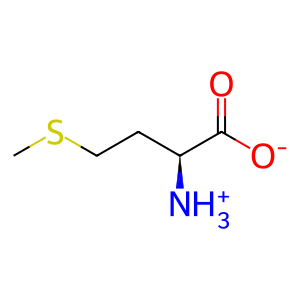
Reaction: MSRA reduces L-methyl-(S)-S-oxide to L-Methionine
- in pathway: Protein repair
Methionine Sulfoxide Reductase A (MSRA) is a peptide-methionine-(S)-S-oxide reductase (1.8.4.11.) (Kim & Gladyshev 2007, Sreekumar et al. 2011) that can reduce both free and protein-based methionine-(S)-S-oxide (Brot et al. 1981, Boschi-Muller et al. 2008). It has been implicated in processes ranging from protection of cells against oxidative damage to the maintenance of cellular homeostasis, prevention of disease and extension of longevity (Kim & Gladyshev 2007, Brennan & Kantorow 2009). MRSA has little or no target specificity and is therefore likely to act on surface-exposed methionine sulphoxide residues of many proteins (Weissbach et al. 2002, Kantorow et al. 2012).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
L-Met [cytosol]
L-methionine (S)-S-oxide [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-5676940
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
L-methionine (S)-S-oxide
Reaction output - small molecules:
L-methionine zwitterion
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-5676940