Reaction: KAT5 acetylates ATM at DNA DSBs
- in pathway: Sensing of DNA Double Strand Breaks
The histone acetyltransferase Tip60 (KAT5), in addition to forming a histone acetyltransferase complex with NuA4, forms another complex with ATM dimers. The ATM dimer:KAT5 complex is formed in the absence of DNA damage, but the acetyltransferase activity of KAT5 is activated by double-strand DNA breaks (DNA DSBs) (Sun et al. 2005). In response to DNA DSBs, the MRN complex targets KAT5 to chromatin, where KAT5 associates with histone H3 trimethylated on lysine 10 (commonly known as H3K9me3 mark). Besides the MRN complex, the ability of KAT5 to access H3K9me3 depends on the DNA damage-induced displacement of HP1beta (CBX1) from H3K9me3 (Ayoub et al. 2008). Binding to H3K9me3 activates the acetyltransferase activity of KAT5 (Sun et al. 2009). KAT5 acetylates ATM on lysine residue K3016 in the highly conserved C-terminal FATC domain of ATM. ATM acetylation is needed for the activation of ATM kinase activity in response to DNA damage (Sun et al. 2007).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
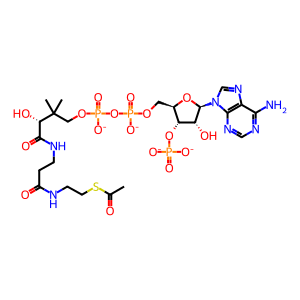
CoA-SH [nucleoplasm]
Ac-CoA [nucleoplasm]
CoA-SH [nucleoplasm]
Ac-CoA [nucleoplasm]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-5682044
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
acetyl-CoA(4-)
acetyl-CoA(4-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
coenzyme A(4-)
coenzyme A(4-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-5682044