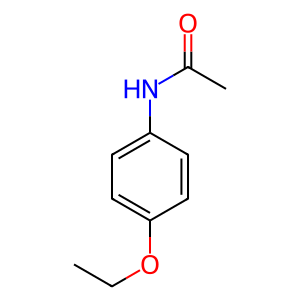
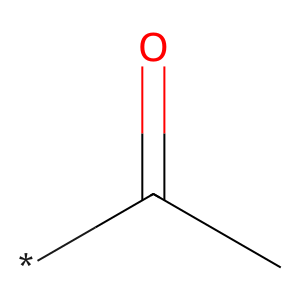
Reaction: AADAC deacetylates PHEN
- in pathway: Phase I - Functionalization of compounds
Esterases contribute to the metabolism of ~10% of therapeutic drugs. Esterases hydrolyse compounds that contain ester, amide, and thioester bonds, which result in prodrug activation or detoxification. Arylacetamide deacetylase (AADAC) is involved in the hydrolysis of flutamide, phenacetin, and rifamycins. AADAC is associated with adverse drug reactions as hydrolytic metabolites of flutamide and phenacetin are associated with hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity/hematotoxicity, respectively. Phenacetin (PHEN) is a mild analgesic/antipyretic drug, widely used from its introduction in 1887 until its ban in 1983. It was banned because of its adverse effects, which include increased risk of certain cancers and kidney damage. It is metabolised into paracetamol, which replaced it as an over-the-counter medication following the ban on PHEN. AADAC hydrolyses PHEN to the p-phenetidine metabolite which is a nephrotoxicant (Watanabe et al. 2010, Fukami & Yokoi 2012).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
acetyl group [cytosol]
4-ethoxyaniline [cytosol]
H2O [cytosol]
PHEN [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-5689000
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
phenacetin
Reaction output - small molecules:
acetyl group
4-ethoxyaniline
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-5689000