Reaction: UCHL1, UCHL3 cleave ubiquitin adducts
- in pathway: UCH proteinases
UCHL1 and UCHL3 can hydrolyze several short C-terminal ubiquitin adducts to generate ubiquitin monomers (Wilkinson et al. 1989, Wada et al. 1998, Larsen et al. 1998). This liberates small molecule nucleophiles that may have inadvertently reacted with Ub C-terminal thiolesters. Because these enzymes can cleave small peptides from the C-terminus of Ub, they could also function in recycling Ub from incomplete proteasomal or lysosomal protein degradation. UCHL3, but not UCHL1, is able to cleave the C-terminus of Neural precursor cell expressed developmentally downregulated protein 8 (NEDD8), a ubiquitin-like protein that activates the largest ubiquitin E3 ligase family, the cullin-RING ligases (Wada et al. 1998, Enchev et al. 2015). UCHL1 and 3 are specifically expressed in neurons, cells of the diffuse neuroendocrine system and their tumors. A polymorphism (S18Y) in UCHL1 is associated with a reduced risk for Parkinson's disease (Wang et al. 2002) and its overexpression is protective in models of Alzheimer's disease (Gong et al. 2006). UCHL1 has been shown to interact with alpha-synuclein, but as a ubiquitin ligase rather than as a ubiquitin hydrolase (Liu et al. 2002). It is K63-polyubiquitinated by Parkin in cooperation with the Ubc13/Uev1a E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme complex, promoting UCH-L1 degradation by the autophagy-lysosome pathway (McKeon et al. 2015).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
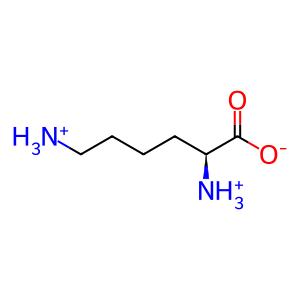
L-lysine [cytoplasm]
H2O [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-5690319
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
Reaction output - small molecules:
L-lysinium(1+)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-5690319