Reaction: PPT1 hydrolyses palmitoylated proteins
- in pathway: Fatty acyl-CoA biosynthesis
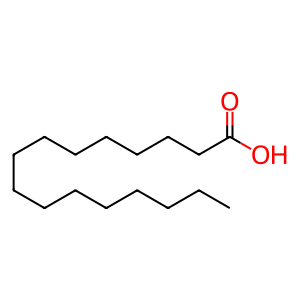
The maintenance/regulation of cellular levels of free fatty acids and fatty acyl-CoAs (the activated form of free fatty acids) is extremely important, as imbalances in lipid metabolism can have serious consequences for human health. Free fatty acids can act as detergents to disrupt membranes so their generation is normally tightly regulated to states where they will be rapidly consumed or sequestered. Acyl-coenzyme A thioesterases (ACOTs) hydrolyse the thioester bond in medium- to long-chain fatty acyl-CoAs (of C12-C18 lengths) (MCFAcylCoA, LCFAcylCoA) to their free fatty acids (MCFA, LCFA) (Cohen 2013, Hunt et al. 2012, Kirkby et al. 2010). Lysosomal thioesterase PPT1 is able to specifically hydrolyse palmitic acid (PALM) from palmitoylated proteins (PALM:protein) (Camp & Hofmann 1993, Camp et al. 1994).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
protein [lysosomal lumen]
PALM [lysosomal lumen]
H2O [lysosomal lumen]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-5690517
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
Reaction output - small molecules:
protein
hexadecanoic acid
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-5690517