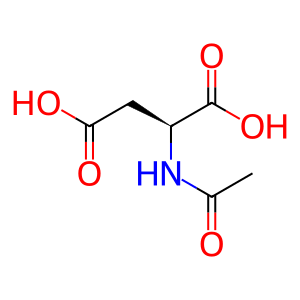
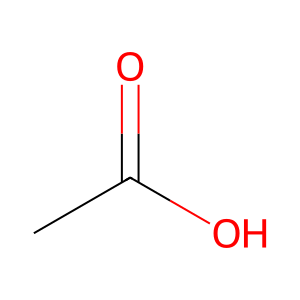
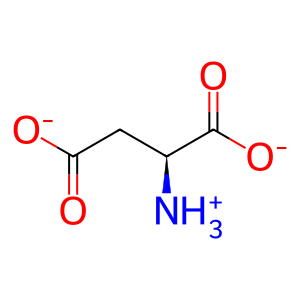
Reaction: ASPA deacetylates NAA to acetate and L-aspartate
- in pathway: Aspartate and asparagine metabolism
Aspartoacylase (ASPA) is a cytosolic zinc metalloenzyme highly expressed in brain white matter, skeletal muscle, kidney, adrenal glands, lung and liver. ASPA catalyses the hydrolysis of N-acetylaspartic acid (NAA) to produce acetate (CH3COO-) and L-aspartate (L-Asp). NAA occurs in high concentration in brain and is thought to play a significant part in the maintenance of intact white matter. In other tissues it acts as a scavenger of NAA from body fluids. Defects in ASPA lead to Canavan disease (CAND; MIM:271900), a fatal neurological disorder of infants characterised by white matter vacuolisation and demyelination (Herga et al. 2006, Le Coq et al. 2006, Bitto et al. 2007).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
CH3COO- [cytosol]
L-Asp [cytosol]
H2O [cytosol]
NAA [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-5691507
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
N-acetyl-L-aspartic acid
Reaction output - small molecules:
acetic acid
L-aspartate(1-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-5691507