Reaction: CEMIP hydrolyses HA
- in pathway: Hyaluronan biosynthesis and export
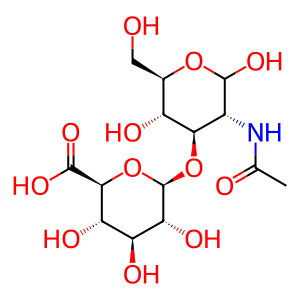
The cell migration-inducing and hyaluronan-binding protein CEMIP (KIAA1199) is able to depolymerise high molecular weight hyaluronic acid (HA) polymers into intermediate-sized products. It randomly hydrolyses of 1-4 linkages between N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosamine and D-glucuronate residues of HA. CEMIP may play a key role in HA catabolism in the dermis of the skin and arthritic synovium (Yoshida et al. 2013).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
GlcA-b1,3-GlcNAc [extracellular region]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-5693356
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
Reaction output - small molecules:
beta-D-GlcpA-(1->3)-D-GlcpNAc
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-5693356